INTERMITTENT HYPOXIC-HYPEROXIC THERAPY (IHHT)
TARGETS
Physical
Body
Condition
Cognitive
Function
Overall
Well-being
Post Viral
Recovery
What is Intermittent Hypoxic-Hyperoxic Therapy (IHHT)?
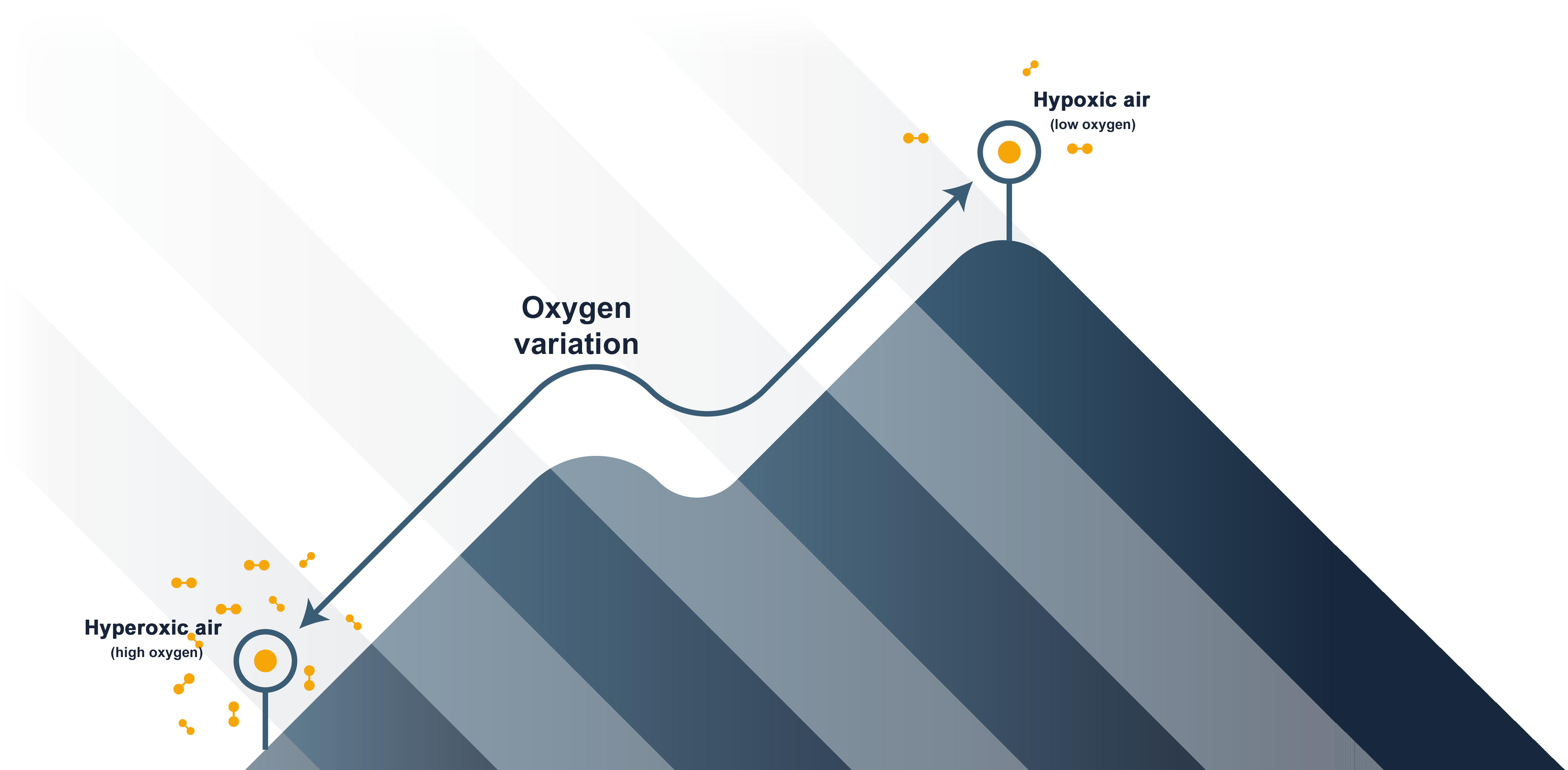
ReOxy’s IHHT provides repeated, alternating intervals of breathing a hypoxic (low oxygenated)
air mixture followed by a hyperoxic (oxygen enriched) air mixture
This innovative therapy mimics natural high-altitude conditions, where oxygen levels are lower.
Our bodies have a natural ability to adapt to such variations in oxygen and this adaptive
reaction induces changes within our organs, tissues and cells to enhance
the body’s overall resilience and performance.
The benefits of these adaptive effects are well known
and top athletes train under such conditions to
improve their performance, stimulate cellular
regeneration & enhance metabolic function.

Why ReOxy?
The therapy is based on short periods of controlled hypoxia with intermittent recovery intervals. The recovery periods are rich in oxygen to increase the positive effects and efficiency of the hypoxic therapy.
 Every person is unique and needs a specific program. ReOxy provides a personalised IHHT experience, where air mixtures and the timing of the intervals are tailored for each individual based on the results of a test session conducted prior to your first treatment.
Every person is unique and needs a specific program. ReOxy provides a personalised IHHT experience, where air mixtures and the timing of the intervals are tailored for each individual based on the results of a test session conducted prior to your first treatment.
During a session, advanced AI-software reads and analyses changes in your vital parameters (including your oxygen saturation level Sp02 and heart rate) and adjusts the supplied air mixtures.
The alternating periods of reduced oxygen (hypoxia) and increased oxygen (hyperoxia), lead to more efficient transport and utilisation of oxygen by body tissue and train your body to use oxygen more efficiently, delivering the positive effects of high altitude right to you.
SIT. BREATHE, RELAX AND OBTAIN THE BENEFITS
It’s that simple
- Sit down and put on the mask and sensor
- Breathe normally and our AI-powered software will calculate the best training program for you
- The program starts – relax for the 40-minute session
- After the session, you can perform all your normal activities without restriction
View this post on Instagram
POSITIVE EFFECTS
CAN REACH THE ENTIRE BODY
Nervous System
Cardiovascular System
Respiratory System
Bones & Joints
Metabolism
Who can benefit?
Whether you’re someone seeking assisted recovery, someone wanting to enhance your overall health and well-being, or an athlete looking to improve performance, consider ReOxy’s IHHT.
Discover the transformative effects of IHHT. To embark on your journey to better health and vitality, reach out to one of the Clinics listed below. For any other information, please Contact Us.
NSW
~
~
VIC
QLD
COMING SOON!
References
https://www.aimediq.com/method-overview/
https://www.aimediq.com/physiological-effects/
Zhang Q, Yan Q, Yang H, Wei W. Oxygen sensing and adaptability won the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or medicine. Genes Dis. 2019;6(4):328-332. Published 2019 Oct 19. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2019.10.006 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6889041/
Uzun AB, Iliescu MG, Stanciu LE, et al. Effectiveness of Intermittent Hypoxia-Hyperoxia Therapy in Different Pathologies with Possible Metabolic Implications. Metabolites. 2023;13(2):181. Published 2023 Jan 25. doi:10.3390/metabo13020181 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36837800/
Serebrovska ZO, Serebrovska TV, Kholin VA, et al. Intermittent Hypoxia-Hyperoxia Training Improves Cognitive Function and Decreases Circulating Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(21):5405. Published 2019 Oct 30. doi:10.3390/ijms20215405 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31671598/
Zhang Q, Zhao W, Li S, Ding Y, Wang Y, Ji X. Intermittent Hypoxia Conditioning: A Potential Multi-Organ Protective Therapeutic Strategy. Int J Med Sci. 2023;20(12):1551-1561. Published 2023 Sep 18. doi:10.7150/ijms.86622 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37859700/
Ehrenreich H, Gassmann M, Poustka L, et al. Exploiting moderate hypoxia to benefit patients with brain disease: Molecular mechanisms and translational research in progress. Neuroprotection. 2023;1(1):9-19. doi:10.1002/nep3.15 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37671067/



 The New Amazing Nectar Page Builder
The New Amazing Nectar Page Builder